
At the DNA replication fork, a DNA helicase (DnaB or MCM complex) precedes the DNA synthetic machinery and unwinds the duplex parental DNA in cooperation with the SSB or RPA. Generally, DNA replication follows a multistep enzymatic pathway. They also suggest that FEN1 may attenuate the various activities of Polδ during DNA repair and recombination.A complex network of interacting proteins and enzymes is required for DNA replication. Our findings call for investigating additional pathways that may accelerate RNA removal in human cells, such as RNA pre-removal by RNase Hs, which, as demonstrated herein, enhances the maturation rate ~10-fold. These mechanisms are coordinated by PCNA, which encircles DNA, and dynamically recruits Polδ, FEN1, and Lig1 to compete for their substrates. Ligase 1 (Lig1) can release the nick from FEN1 and actively drive the reaction toward ligation. Here, we show that human Polδ is inefficient in releasing the nick product from FEN1, resulting in non-processive and remarkably slow RNA removal. Iterative cycles between Polymerase δ (Polδ) and Flap endonuclease-1 (FEN1) remove the primer, with an intermediary nick structure generated for each cycle. They also suggest that FEN1 may attenuate the various activities of Polδ during DNA repair and recombination.ĪB - The final steps of lagging strand synthesis induce maturation of Okazaki fragments via removal of the RNA primers and ligation. N2 - The final steps of lagging strand synthesis induce maturation of Okazaki fragments via removal of the RNA primers and ligation. Martin Reijns for the generous gift of human RNase H2 expression plasmid (pGEX6P1-hsRNASEH2BCA, Addgene plasmid #108692). Petr Cejka for the generous gift of human DNA2 expression plasmid. Wold for the generous gift of human RPA expression plasmid. Hamdan’s lab for the helpful discussions. We thank Yujing Ouyang for the preparation of the functionalized coverslips.
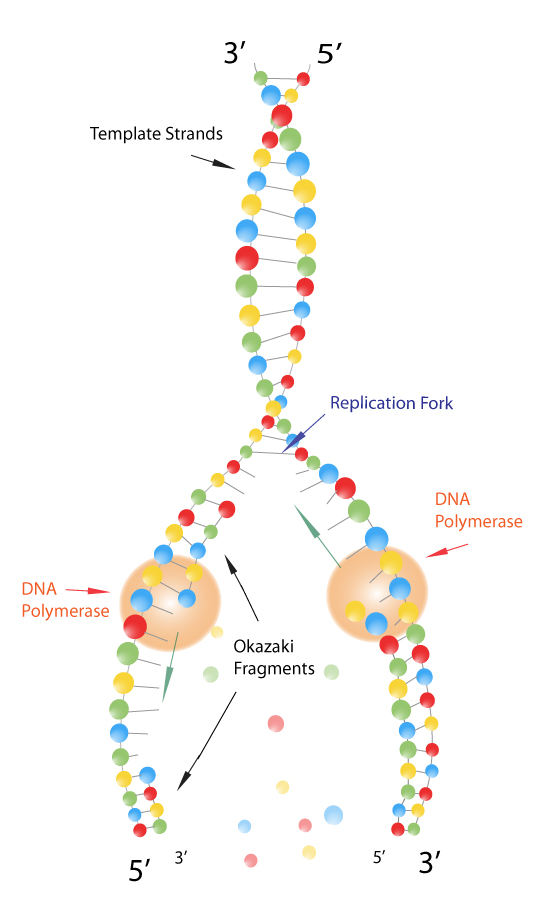
T1 - Mechanistic investigation of human maturation of Okazaki fragments reveals slow kineticsĪcknowledged KAUST grant number(s): CRG8 URF/1/Īcknowledgements: This work was supported by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology under Competitive Research Award Grant CRG8 URF/1/ to S.M.H. They also suggest that FEN1 may attenuate the various activities of Polδ during DNA repair and recombination.", Abstract = "The final steps of lagging strand synthesis induce maturation of Okazaki fragments via removal of the RNA primers and ligation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
