
(1991), Production of Organic Chemicals via Bioconversion: A Review of the Potential, DOE Report No. Annual Report for 1955/56, HW 41500:35, Hanford Biological Research, Richland, WA. (1956), Effect of Chronic Exposure of Sodium Bichromate on Young Chinook Salmon and Rainbow Trout. OHER Subsurface Science Program, PNL, Richland, WA. (1991), Nature of Chemical Contaminants on DOE Lands and Identification of Representative Contaminant Mixtures for Basic Subsurface Science Research. Comparisons to conventional Cr(6 +) treatment technologies indicate that a bioprocess has several economic and operational advantages. 7.6) and high filter loading rate (6 gpm ft-2) had negative impacts. The beads contain internal macropores which were shown by scanning electron microscopy to house dense concentrations of bacteria. (VI) to Cr(III) using ferrous sulfate followed by coagulation and filtration.
4.8 4.8 out of 5 stars 159 ratings 4 answered questions. They are usually obtained by oxidation-reduction reactions from chromium (III).
#CR 6 TO CR 3 SERIES#
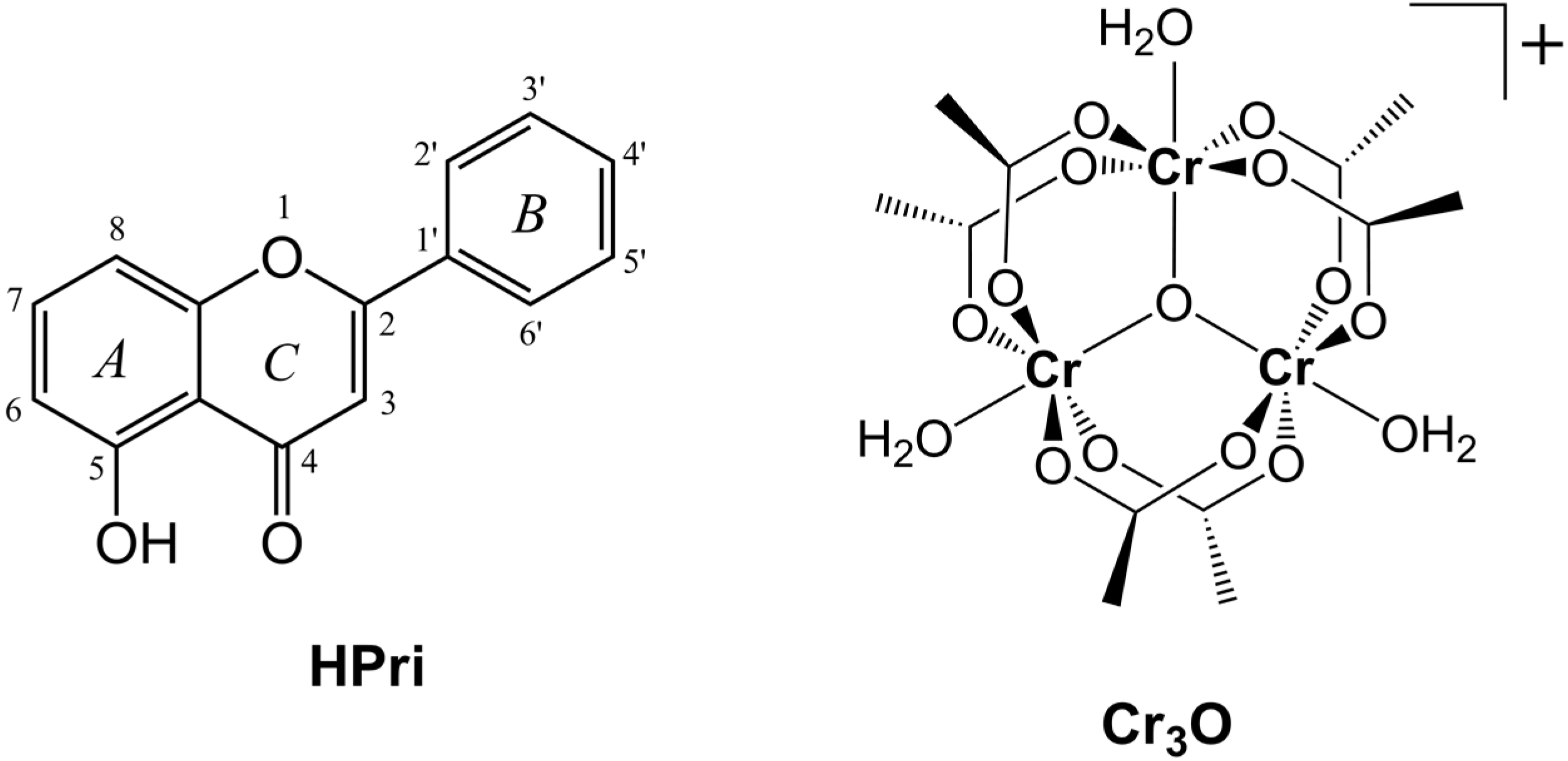
An increase in volumetric productivity (from 4 mg Cr(6 +)/L/h to 260 mg Cr(6 +)/L/h, probably due to an increase in biomass density, was obtained using Bio-Sep beads. Creality Original 12pcs Ender 3 Series 0.4mm MK Nozzles, for Sprite Extruder Nozzle/Ender 3 S1/Pro/Ender 3/V2/Pro/Max/CR-6 SE/MAX Nozzle, for Ender-3 Serise/Ender-5 Series/Ender 3 Neo Series. Salts of chromium (II) have a bluish color. A bioprocess for Cr(6 +) reduction has been demonstrated using a packed-bed bioreactor containing ceramic packing, and then compared to a similar bioreactor containing DuPont Bio-Sep beads. Alternatively, Cr(6 +) can be biochemically reduced to Cr(3 +) by anaerobic microbial consortia which appear to use Cr(6 +) as a terminal electron acceptor.

Reduction of the mobile Cr(6 +) to the less mobile and less toxic trivalent chromium, Cr(3 +), can be achieved with conventional chemical reduction technologies. EGG-BG-9033.Hexavalent chromium, Cr(6 +), is a common and toxic pollutant in soils and waters. Hexavalent Cromium or Chromium-6 (Cr-6) is the product of the oxydation of Cr-3 or Cr-4 contained in the alloy of certain stainless steel parts from the exhaust. It’s an attempt to catch up to the big boys and to finally have something that’s not going to be labeled as just another budget 3D printer. (1991), Production of Organic Chemicals via Bioconversion: A Review of the Potential, DOE Report No. tom Why you should get the Ender-3 v2 instead of the CR-6 SE Watch on The Creality CR-6 SE. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the salt sodium dichromate. All have 6 ligands (coordination number 6)CrCl3.6H2O Contains primarily Cr(H2O)4Cl2+ On standing in solution, gives a mixture of: Cr(H2O)4Cl2+ (light green) Cr(H2O)5Cl2+ (dark green) Cr(H2O)63+ (blue gray) Can measure the ion charge by the behavior on an ion exchange column. (1956), Effect of Chronic Exposure of Sodium Dichromate on Young Chinook Salmon and Rainbow Trout. Hexavalent chromium (chromium(VI), Cr(VI), chromium 6) is chromium in any chemical compound that contains the element in the +6 oxidation state (thus hexavalent). The beads contain internal macropores which were shown by scanning electron microscopy to house dense concentrations of bacteria. An increase in volumetric productivity (from 4 mg Cr(6 +)/L/h to 260 mg Cr(6 +)/L/h, probably due to an increase in biomass density, was obtained using Bio-Sep beads. European Union Directive 2003/53/EC restricts the use of cement and cement products to those. Alternatively, Cr(6 +) can be biochemically reduced to Cr(3 +) by anaerobic microbial consortia which appear to use Cr(6 +) as a terminal electron acceptor. method to determinations of Cr(VI) in soils and cement.56. Hexavalent chromium, Cr(6 +), is a common and toxic pollutant in soils and waters.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
